Did you know that goldfish can mate with different types of goldfish? It's fascinating how these beautiful fish can reproduce and create new variations. In this article, we'll delve into the world of goldfish mating and explore the different outcomes that can occur when different types of goldfish breed with each other.
When it comes to goldfish, there are numerous breeds with distinct features and characteristics. From the fancy varieties like the Oranda or the Ryukin to the sleek and slender Comet or Shubunkin, each type of goldfish brings its own unique traits to the mating process. And surprisingly, they can all interbreed with each other!
The offspring of such unions can result in interesting combinations, with a mix of traits from both parents. For example, if a Comet goldfish mates with a Ryukin goldfish, their offspring might have the body shape of the Comet and the fancy tail of the Ryukin. It's like creating a unique fusion of different goldfish breeds!
In the upcoming article, we'll explore the topics of goldfish reproduction, breeding techniques, and the potential outcomes of different types of goldfish mating. Whether you're a goldfish enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of nature, this article will provide you with a deeper understanding of how these beautiful fish come to be. Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of goldfish mating!

Will Different Types Of Goldfish Mate
Goldfish are one of the most popular and recognized fish species in the world. Known for their stunning colors and graceful swimming behavior, they are a favored pet for many fish enthusiasts. But have you ever wondered if different types of goldfish can mate with each other? In this article, we will explore the possibilities of goldfish interbreeding and the outcomes that can arise from these unique unions.
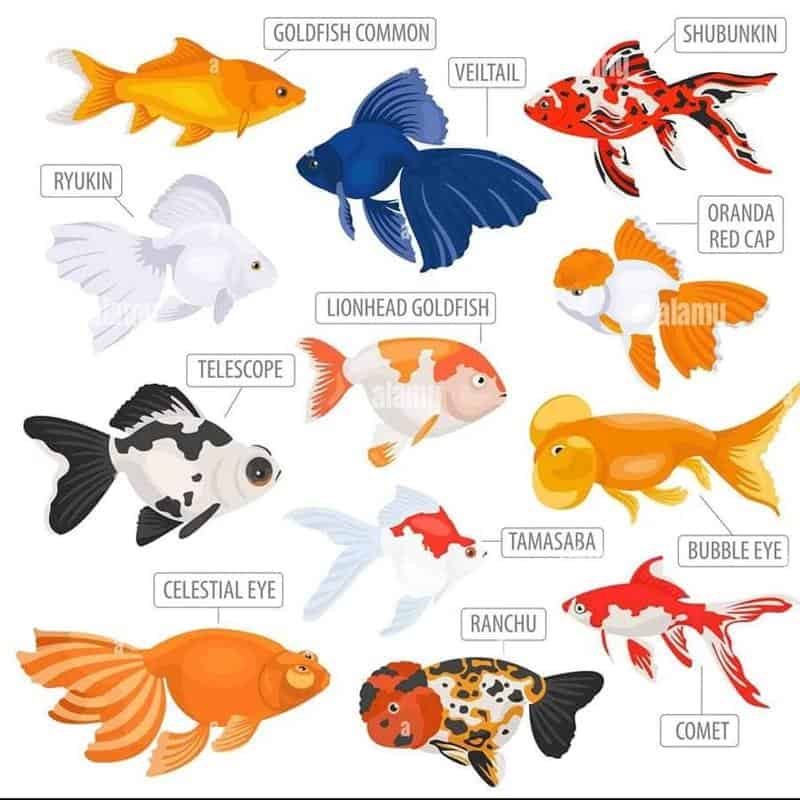
The Different Types of Goldfish
Goldfish come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and colors. Here are some of the most common types:
Common Goldfish
The common goldfish, also known as the American or London shubunkin, is the most basic and widely found goldfish type. They have a sleek body shape and are usually orange or orange-red in color. Common goldfish are hardy and adaptable, making them a popular choice for beginners.
Comet Goldfish
Comet goldfish are similar in appearance to common goldfish, but they have a longer and more slender body. Their tail fins are also longer and more dramatic. Comets are known for their exceptional swimming abilities and can reach impressive speeds in the water.
Shubunkin Goldfish
Shubunkin goldfish have a unique color pattern that sets them apart from other goldfish varieties. They have a predominantly blue background with speckles of red, yellow, and black throughout their body. Shubunkins are active and fast swimmers, often displaying vibrant colors as they dart through the water.
Fantail Goldfish
Fantail goldfish are easily recognized by their double tail fins, which give them a beautiful and elegant appearance. They have a rounded body shape and come in a variety of colors, including red, white, black, and calico. Fantails are gentle and friendly, making them a favorite among goldfish enthusiasts.
Oranda Goldfish
Oranda goldfish are known for their distinctive brain-like growth, called a wen, on top of their head. They have a rounded body, and their tail fins are typically long and flowing. Orandas are available in a wide range of colors, including red, white, black, and calico. Due to their elegant appearance, they are highly sought after by collectors.
Ryukin Goldfish
Ryukin goldfish have a humpbacked body shape, which sets them apart from other goldfish varieties. This unique feature gives them a regal and majestic appearance. Ryukins have a variety of color patterns, including metallic and calico. They are known for their active swimming behavior and striking colors.
Telescope Goldfish
Telescope goldfish are characterized by their protruding eyes, which give them a distinctive and captivating appearance. They have a rounded body and a long, flowing tail fin. Telescopes are available in various colors, including red, black, and metallic. They are peaceful and sociable fish that thrive in ponds or large aquariums.
Black Moor Goldfish
Black Moor goldfish are easily recognizable due to their jet-black coloration and bulging eyes. They have a rounded and chubby body shape, with a long, flowing tail fin. Black Moors are calm and gentle, making them a popular choice for goldfish keepers.
Bubble Eye Goldfish
Bubble Eye goldfish are known for the fluid-filled sacs that develop underneath their eyes. These sacs can vary in size and shape, and they enhance the goldfish's adorable and unique appearance. Bubble Eyes have a rounded body and a short, double-tail fin. They are peaceful and gentle fish that require special care due to their delicate eye sacs.
Lionhead Goldfish
Lionhead goldfish are prized for their majestic appearance, with a prominent hood or growth on top of their head. They have a rounded body shape and a short, double-tail fin. Lionheads come in various colors, including red, white, black, and metallic. They are gentle and peaceful fish, making them a favorite among collectors.
Now that we have familiarized ourselves with the different types of goldfish, let's delve into the intriguing world of goldfish mating behavior.
Goldfish Reproduction
Like many fish species, goldfish reproduce by laying eggs. Goldfish are egg scatterers, meaning that the female releases eggs into the water, and the male fertilizes them externally. The fertilized eggs then develop into fry, which eventually grow into adult goldfish.
The Mating Process
Goldfish mating behavior occurs during the spring and summer months when water temperatures rise. Male goldfish will begin to chase and nudge the female, trying to prompt her to release eggs. Once the female is ready, she will release hundreds or even thousands of eggs into the water.
The male goldfish will then release sperm to fertilize the eggs externally. After the eggs are fertilized, they attach to aquatic plants or other surfaces and begin the incubation process.
Factors Affecting Goldfish Mating
Several factors influence goldfish mating behavior and the success of reproduction. These factors include water temperature, water quality, overall health and condition of the goldfish, and the genetic compatibility between the individuals.
Water temperature is crucial for successful goldfish mating, as it triggers hormonal changes in the fish and stimulates the release of eggs. The ideal temperature for goldfish mating is around 68 to 74 degrees Fahrenheit (20 to 23 degrees Celsius).
Good water quality is essential for the health and well-being of goldfish, as well as their reproductive success. Clean water with the right balance of nutrients and oxygen is vital for the development and survival of goldfish eggs and fry.
The overall health and condition of the goldfish also play a significant role in their ability to reproduce. Goldfish that are malnourished, stressed, or have underlying health issues may have difficulties in mating and producing healthy offspring.
Lastly, genetic compatibility between goldfish individuals can determine the success of the mating process. Goldfish from different varieties or breeds may have different genetic traits, which can affect the viability of their offspring.
Now that we have a basic understanding of goldfish mating behavior, let's explore the intriguing concept of interbreeding between different goldfish types.
Can Different Goldfish Types Mate?
Goldfish of different types can mate and produce offspring, but the success and viability of this interbreeding can vary. Some goldfish types are more closely related and genetically compatible, making successful mating and viable offspring more likely. However, other combinations may result in genetic abnormalities or hybrid offspring with reduced viability.
Possible Outcomes of Interbreeding
When different types of goldfish mate, several outcomes are possible. These outcomes depend on the genetic traits of the parent goldfish and the compatibility between them. Let's explore some of the possible outcomes:
-
Hybrid Offspring: Interbreeding between different goldfish types can result in hybrid offspring. These hybrids may display a combination of traits from both parent fish, resulting in unique and visually striking fish. Hybrid goldfish can have variations in body shape, color patterns, and fin shapes.
-
Genetic Abnormalities: Interbreeding between certain goldfish types may result in genetic abnormalities or deformities in the offspring. These abnormalities can affect the fish's overall health, swimming abilities, and lifespan. It is essential to consider the potential risks of interbreeding and the welfare of the offspring before attempting such breeding experiments.
-
Reduced Viability: Interbreeding between different goldfish types can lead to hybrid offspring with reduced viability. These hybrids may have lower resistance to diseases, weaker immune systems, or reduced fertility. It is crucial to carefully monitor the health of hybrid goldfish and provide them with the proper care and attention they need.
Interbreeding between different goldfish types can be a fascinating and rewarding endeavor for experienced goldfish breeders. However, it is essential to approach interbreeding with caution and consideration for the well-being of the fish involved.
What are Hybrid Goldfish?
Hybrid goldfish are the result of intentional interbreeding between different goldfish types. Breeders purposely pair fish of different varieties to create unique and visually stunning offspring. Hybrid goldfish can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, making them highly sought after among collectors.
Examples of Hybrid Goldfish
There are numerous examples of hybrid goldfish that have been created through selective breeding. Some popular hybrid goldfish include:
-
Ranchu Oranda: The Ranchu Oranda is a hybrid between the Ranchu and Oranda goldfish. It combines the rounded body shape of the Ranchu with the distinctive wen growth of the Oranda, resulting in a visually striking fish.
-
Calico Butterfly: The Calico Butterfly is a hybrid between the Telescopic Goldfish and the Fantail Goldfish. It features the long, flowing fins of the Fantail and the vibrant calico coloration of the Telescopic Goldfish.
-
Pompon Ranchu: The Pompon Ranchu is a hybrid between the Ranchu and Chinese Goldfish. It inherits the rounded body shape of the Ranchu and the unique pompon-like growths on its fins, giving it a stunning and unique appearance.
These are just a few examples of the many hybrid goldfish varieties that have been created through selective breeding. Each hybrid goldfish has its own unique traits and characteristics, making them highly prized among goldfish enthusiasts.
Genetic Problems in Hybrid Offspring
While interbreeding can create visually captivating hybrid goldfish, it can also result in genetic problems in the offspring. Goldfish from different varieties or breeds may carry different genetic traits, some of which may be incompatible when combined.
These genetic problems can manifest as deformities, reduced fertility, or lower overall health and well-being in the hybrid offspring. It is essential for breeders to carefully consider the potential risks and implications of interbreeding before attempting such experiments.
Incompatibility and Aggression
Interbreeding goldfish of different types can also lead to compatibility issues and aggression among the fish. Some goldfish varieties may have different temperaments or aggression levels, which can result in conflicts or stress within the mating pair or among the offspring.
It is crucial to monitor the behavior and well-being of the goldfish involved in interbreeding experiments. If aggression or compatibility issues arise, it may be necessary to separate the fish to ensure their safety and well-being.
Market Value of Hybrid Goldfish
Hybrid goldfish are highly prized among collectors and goldfish enthusiasts. Their unique and visually striking appearance, as well as their rarity, contribute to their market value. Some hybrid goldfish can command high prices in the goldfish trade, especially if they display a combination of desirable traits from both parent varieties.
However, it is important to note that not all hybrid goldfish are in high demand. The market value of a hybrid goldfish ultimately depends on its overall quality, health, and the desirability of its traits among collectors.
Purpose of Selective Breeding
Selective breeding is a practice commonly used in the aquaculture industry to enhance specific traits in fish populations. The purpose of selective breeding in goldfish is to produce offspring that exhibit desired characteristics, such as vibrant colors, unique body shapes, or striking fin patterns.
Selective breeding can be a time-consuming and meticulous process, requiring careful selection of parent fish with desirable traits. It takes patience, knowledge, and experience to successfully breed goldfish with specific traits.
Breeding for Specific Traits
When selectively breeding goldfish, breeders aim to enhance specific traits in the offspring. These traits can include body shape, color, fin length, and the presence of unique growths, such as the wen or eye sacs in certain goldfish varieties.
Breeders carefully choose parent fish with the desired traits and selectively pair them together to produce offspring that display those specific characteristics. The breeding process may take several generations before the desired traits are consistently expressed in the offspring.
Commercial Breeding Operations
Commercial breeding operations play a significant role in the production and availability of goldfish in the market. These operations specialize in breeding specific goldfish varieties, such as the Ranchu, Oranda, or Ryukin, for mass distribution to pet stores and fish enthusiasts.
Commercial breeding operations follow strict breeding protocols and guidelines to ensure the health and quality of their fish. They invest in specialized facilities, proper nutrition, and regular health checks to produce healthy and vibrant goldfish for sale.
Intentional Crossbreeding
Intentional crossbreeding is the deliberate pairing of goldfish from different varieties or breeds to create hybrid offspring. Breeders who engage in intentional crossbreeding aim to produce visually unique and desirable goldfish that stand out from traditional goldfish varieties.
Crossbreeding involves carefully selecting parent fish with complementary traits and genetic compatibility. Breeders must consider the potential risks and challenges of crossbreeding, including genetic abnormalities and reduced viability in the offspring.
Results and Challenges of Selective Breeding
Selective breeding can yield impressive results over time, with the consistent production of goldfish that display specific traits. However, it is not without its challenges. Selective breeding requires knowledge and experience to successfully pair and breed goldfish that exhibit the desired traits.
Breeders must also be aware of the potential risks and challenges associated with selective breeding, such as genetic abnormalities or reduced overall health in the offspring. Regular monitoring and maintenance of breeding stock, as well as proper care of the developing fry, are essential for successful selective breeding operations.
Separate Living Spaces
To maintain goldfish breeds and prevent crossbreeding, it is crucial to provide separate living spaces for different varieties. Goldfish breeds should be housed in separate tanks or ponds to prevent accidental interbreeding.
By providing separate living spaces, breeders can maintain the genetic purity and integrity of each goldfish variety. This ensures that each breed retains its specific traits and characteristics without the risk of crossbreeding.
Monitoring and Care
Proper monitoring and care are essential in maintaining the health and well-being of goldfish breeds. Breeders should regularly check the water quality, temperature, and overall condition of their goldfish to ensure optimal breeding conditions.
Additionally, regular health checks, feeding schedules, and appropriate nutrition are necessary to support the growth and overall health of goldfish breeders. Any signs of illness or stress should be promptly addressed to prevent potential complications and maintain the breeding stock's well-being.
Preventing Crossbreeding
Preventing crossbreeding requires careful planning and management of breeding operations. Breeders must ensure that goldfish breeds are kept separate at all times, including during the mating and egg-laying process.
By separating different goldfish varieties, breeders can prevent accidental interbreeding and maintain the genetic purity of each breed. This allows for the preservation of specific traits, colors, and body shapes within each goldfish variety.

Conclusion
In conclusion, goldfish of different types can mate and produce offspring, but the success and viability of these unions can vary. Interbreeding between different goldfish types can result in visually striking hybrid offspring, but it can also lead to genetic abnormalities or reduced viability.
Breeders who engage in intentional crossbreeding must carefully consider the potential risks and challenges associated with interbreeding. It is essential to prioritize the health and well-being of the fish, as well as the preservation of each goldfish variety's genetic integrity.
Selective breeding plays a significant role in maintaining and enhancing specific goldfish varieties. Breeders can selectively pair goldfish with desirable traits to produce offspring that showcase those specific characteristics. However, selective breeding requires knowledge, patience, and experience to yield consistent results.
By providing separate living spaces, monitoring and caring for breeding stock, and preventing crossbreeding, goldfish enthusiasts and breeders can maintain the genetic purity and overall health of their beloved fish. With proper care and attention, goldfish will continue to flourish in their various forms, captivating and bringing joy to countless fish enthusiasts around the world.